GitLab Self-Hosted
Notice
It is possible to add the Checkmarx One external IP addresses to the customer Firewall allowlist - For more information see Managing Checkmarx One Traffic and AWS S3 Access
Additionally, if the code repository is not internet accessible, it is possible to configure the code repository IP address instead of its hostname during the initial integration with the code repository - as it is not resolved via DNS.
Overview
Checkmarx One supports GitLab integration, enabling automated scanning of your GitLab projects whenever the code is updated. Checkmarx One’s GitLab integration listens for GitLab commit events and uses a webhook to trigger Checkmarx scans when a push, or a pull request occurs. Once a scan is completed, the results can be viewed in Checkmarx One.
In addition, for pull requests, a comment is created in GitLab, which includes a scan summary, list of vulnerabilities and a link to view the scan results in Checkmarx One.
Notice
This integration supports both public and private git based repos.
The integration is done on a per project basis, with a specific Checkmarx One Project corresponding to a specific GitLab repo.
Notice
You can select several repos to create multiple integrations in a bulk action.
Prerequisites
The source code for your project is hosted on a GitLab repo.
You have a Checkmarx One account and have credentials to log in to your account.
Important
Creating new import configurations or editing existing configurations requires
update-tenant-paramspermission. Importing new Projects using an existing configuration requirescreate-projectpermission.Our best practice recommendation is to create a dedicated service user for the purpose of creating the integration. This will ensure that scans created via the integration will have a representative name.
The GitLab user has Maintainer or Owner privileges for this Project, see Code Repository Integrations.
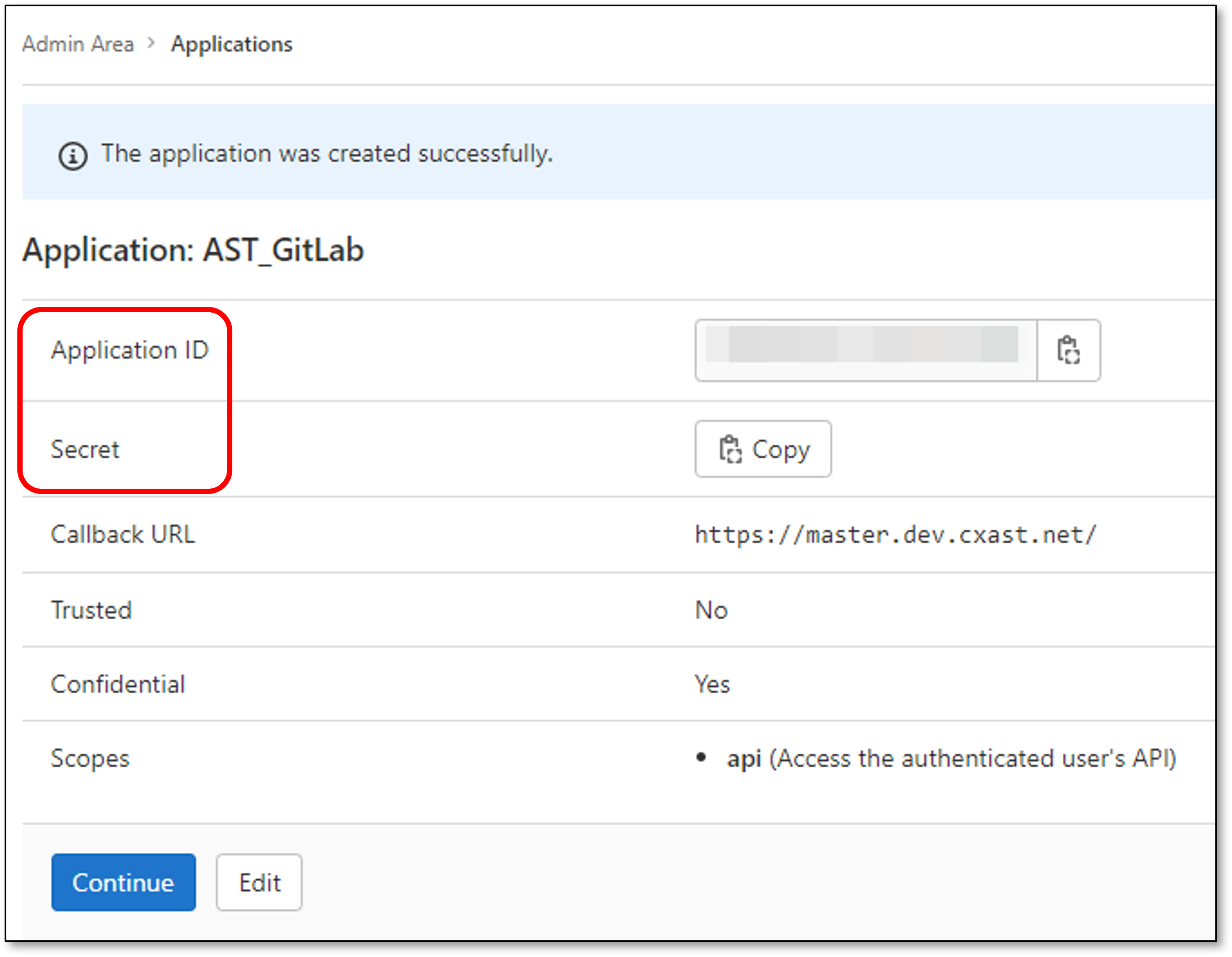
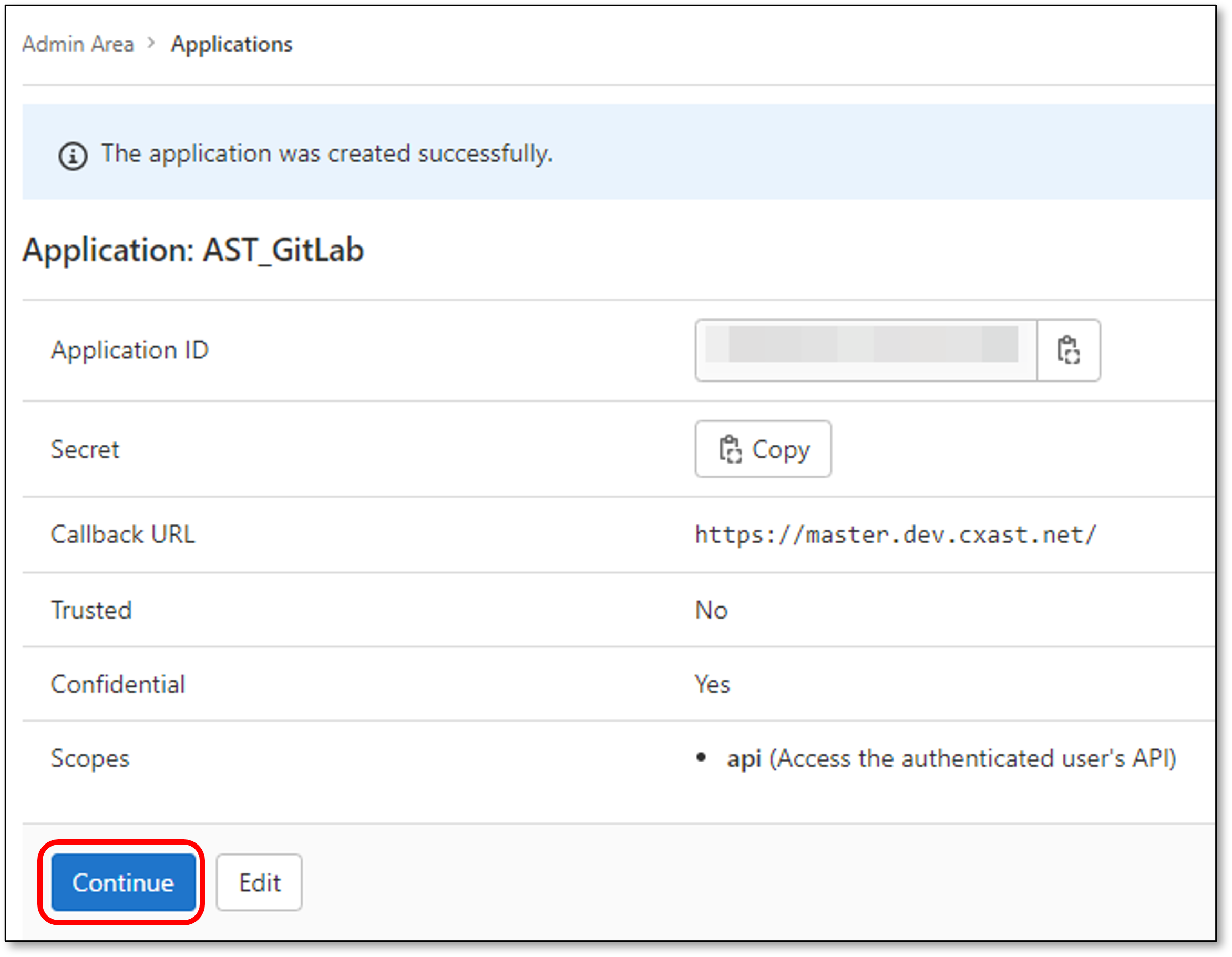
You have your GitLab Client ID & Client Secret - See Retrieving GitLab Application ID & Application Secret.
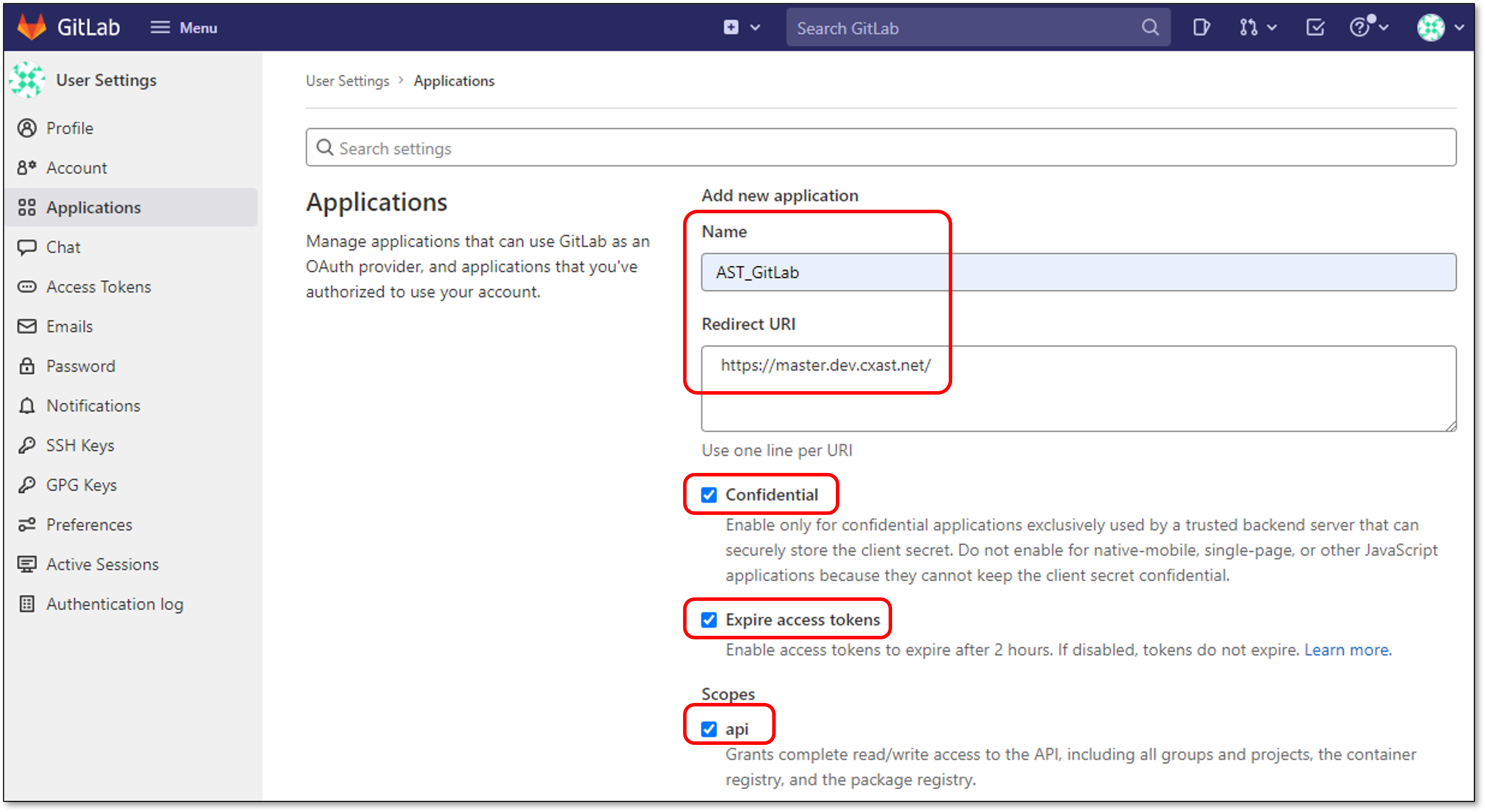
Retrieving GitLab Application ID & Application Secret
Setting up the Integration and Initiating a Scan
This process involves first connecting to your repo by specifying the repo URL and your authentication credentials, and then selecting the repos to import and configuring the Project settings.
It is possible to configure multiple configurations for connecting to GitLab self-hosted code repositories, each using a different URL and/or different authentication credentials. Once the initial configuration is set up, for each subsequent import action you can choose either to use the existing configuration or to create a new one.
To create GitLab self-hosted code repository Projects:
In the Workspace
 , click on New > New Project - Code Repository Integration.
, click on New > New Project - Code Repository Integration. 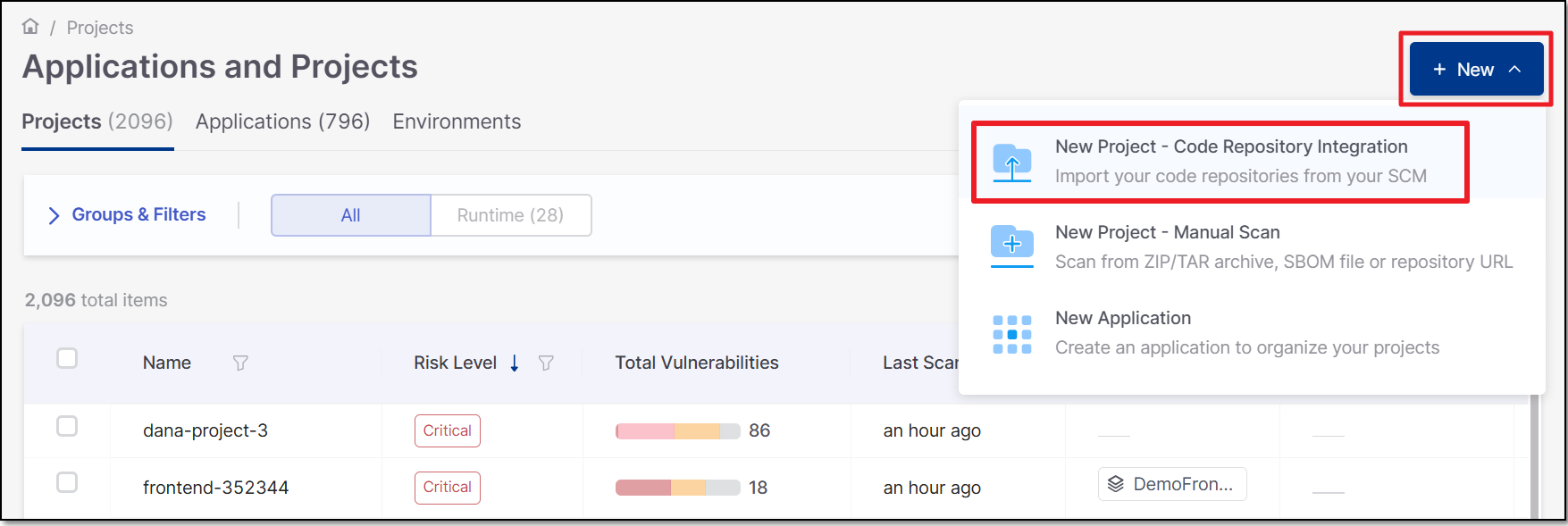
The Import From window opens.
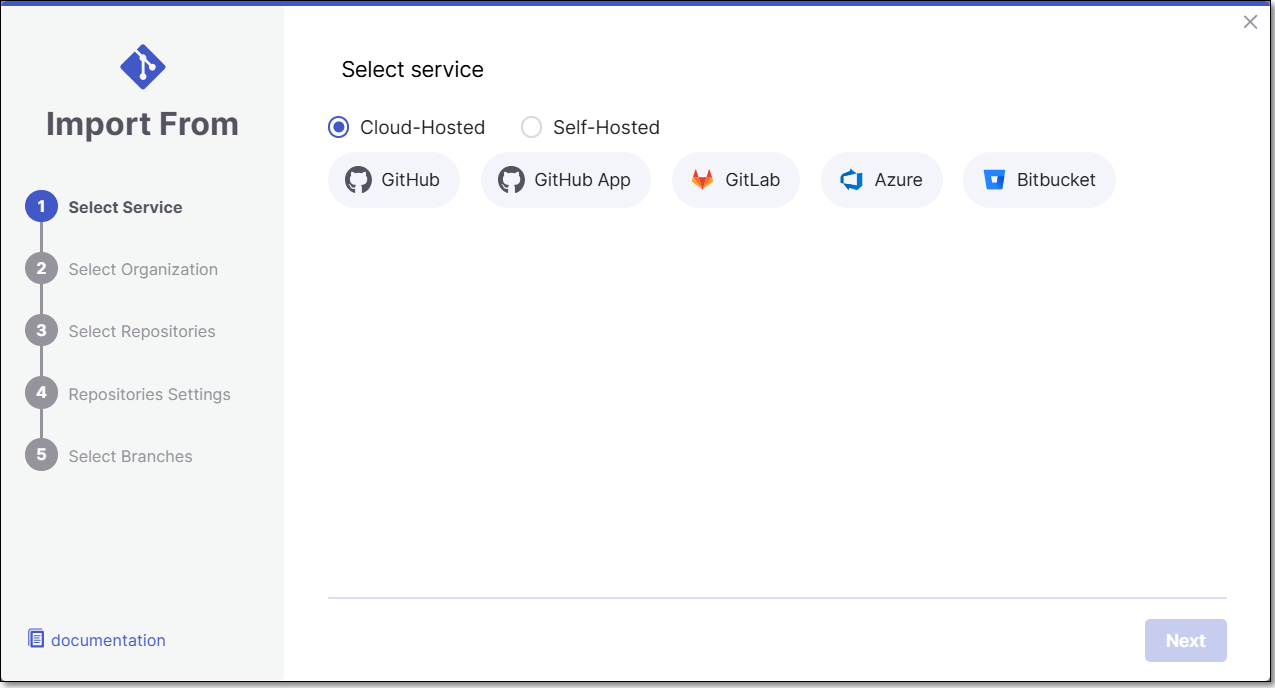
Select Self-Hosted > GitLab.
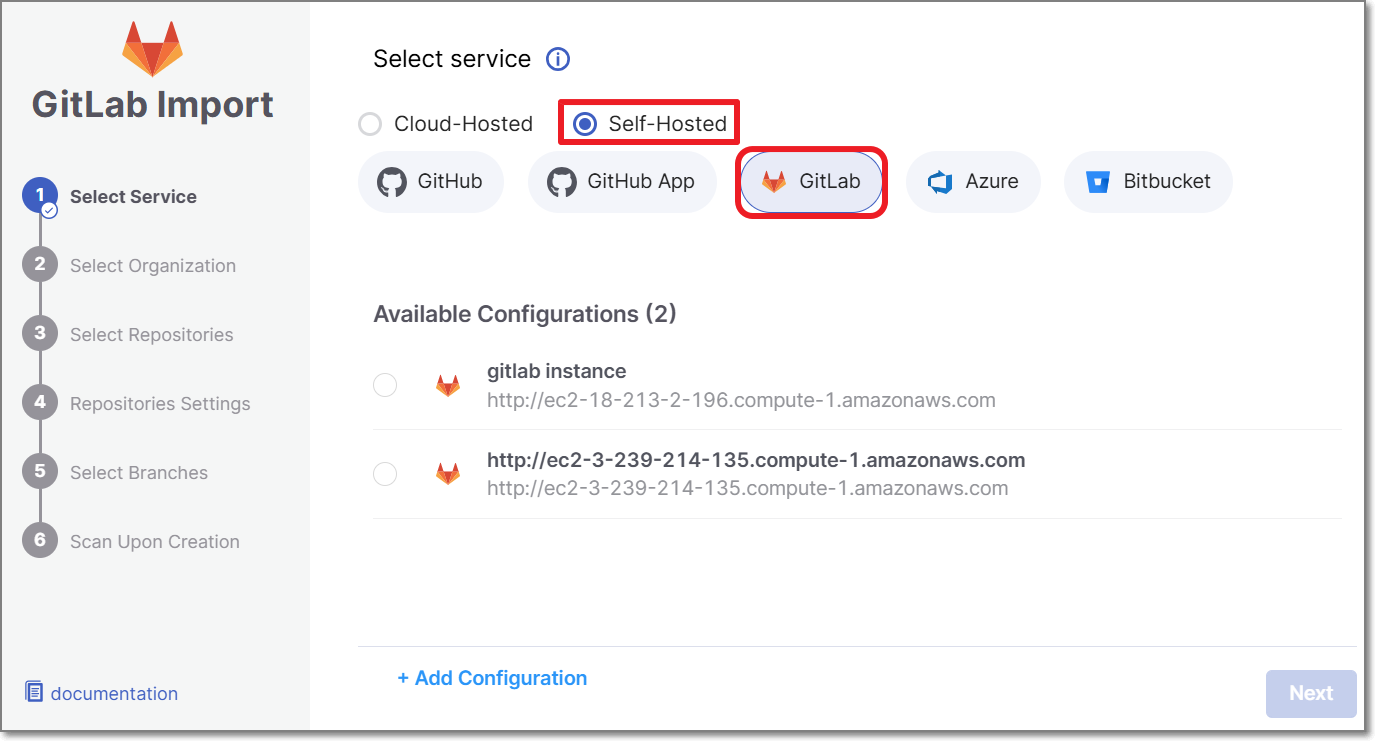
Configure the connection to your code repository, as follows:
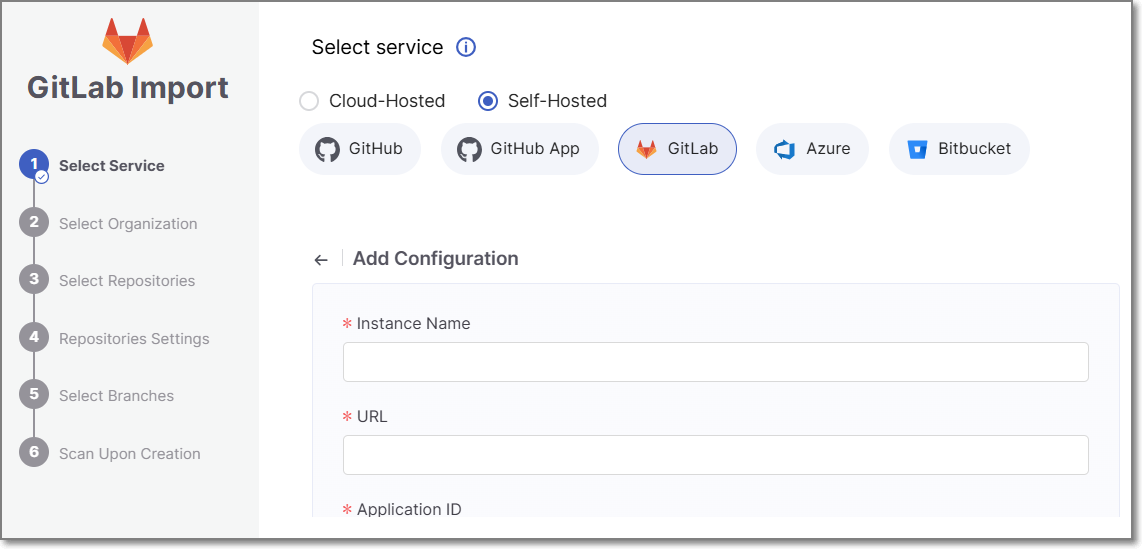
If you are setting up an import configuration for the first time, enter data for the following fields and then click Save & Continue.
Instance Name - Designate a name for this import configuration.
URL - Your GitLab self-managed domain.
For example: https://gitlab.example.com
Application ID - See Retrieving GitLab Application ID & Application Secret for retrieving your Applicaiton ID.
Secret - See Retrieving GitLab Application ID & Application Secret for retrieving your Application Secret.
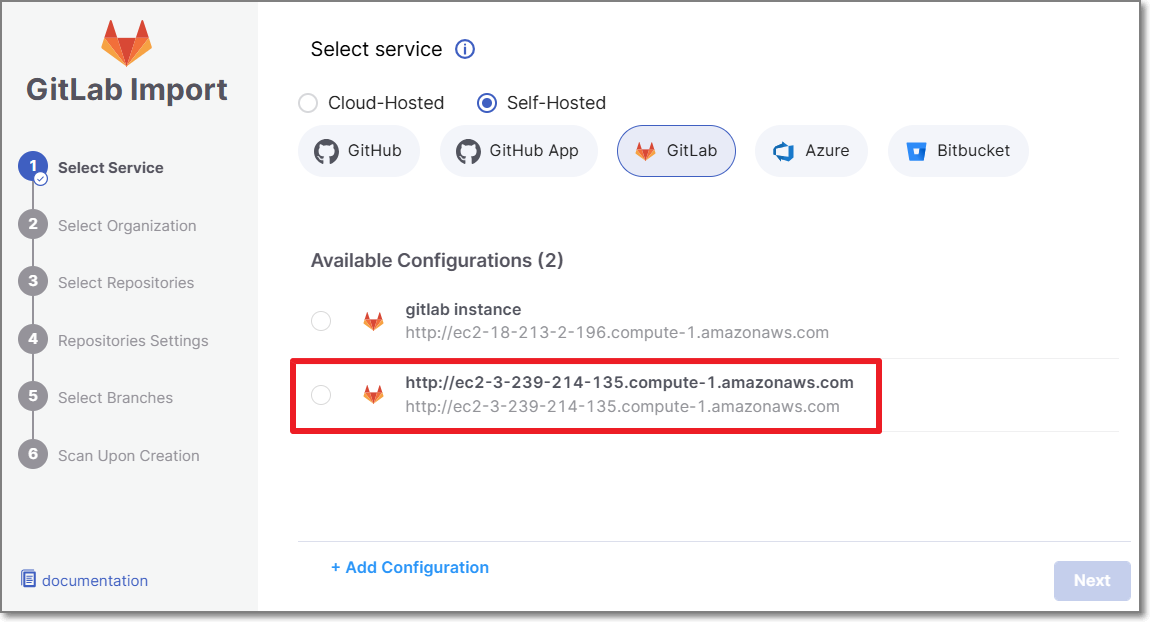
If you are importing Projects using an existing configuration, select the radio button next to the configuration that you would like to use, and then click Next.
If you are adding a new configuration in addition to an existing configuration, click + Add Configuration, then fill in the data for this configuration as described above, and then click Save & Continue.
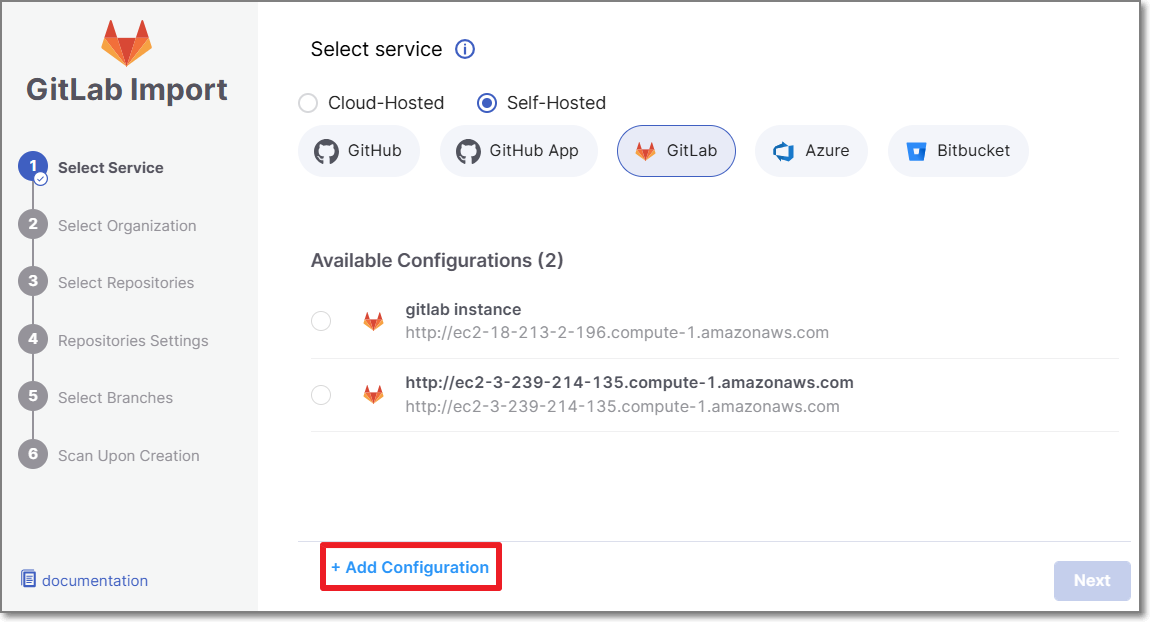
Notice
If you would like to edit an existing configuration (e.g., change the URL or credentials), go to Global Settings > Code Repository.
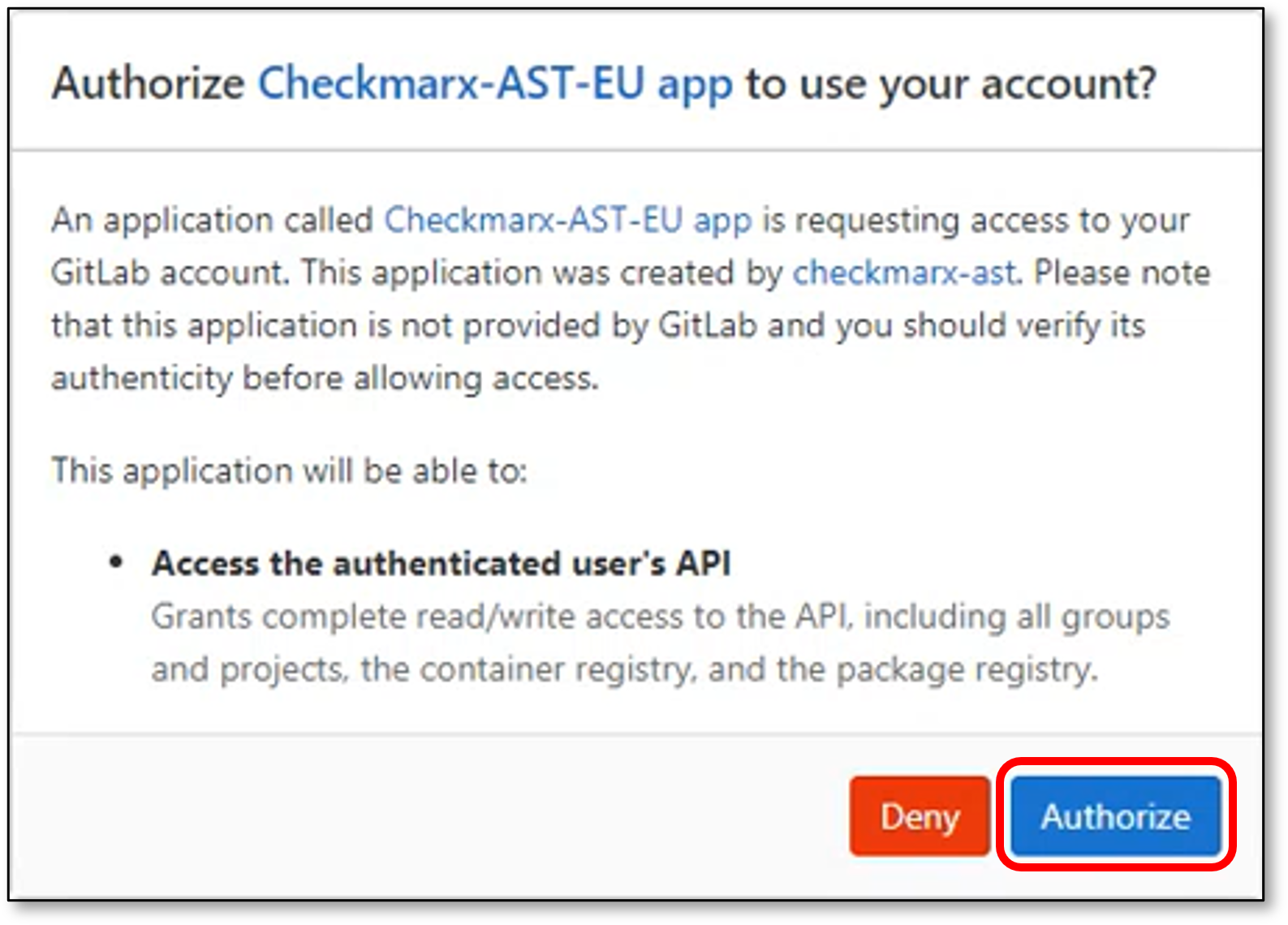
Upon initial log in, approve the GitLab account authorization request via Checkmarx One.
Click Authorize.
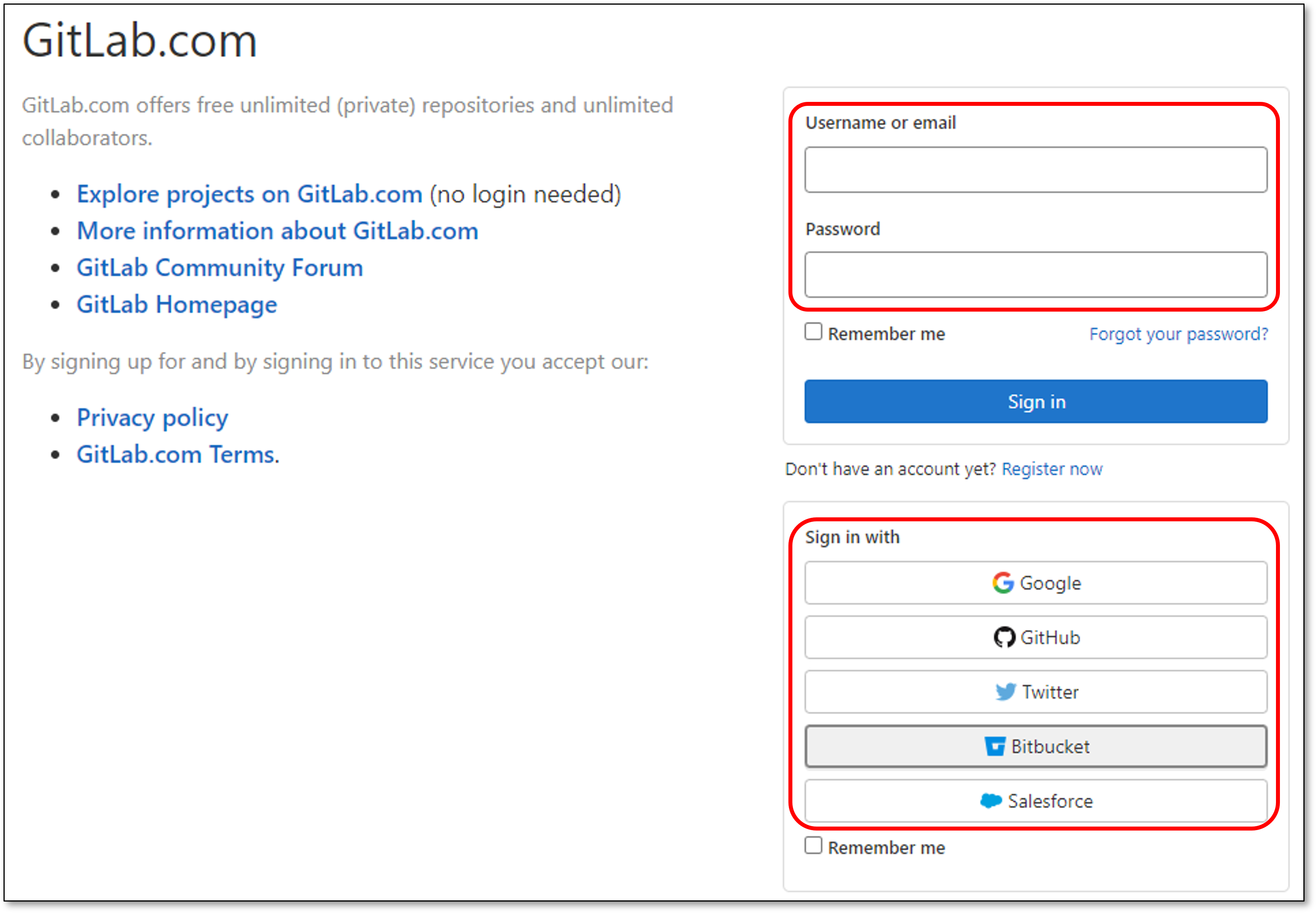
Sign in to GitLab using one of the following options:
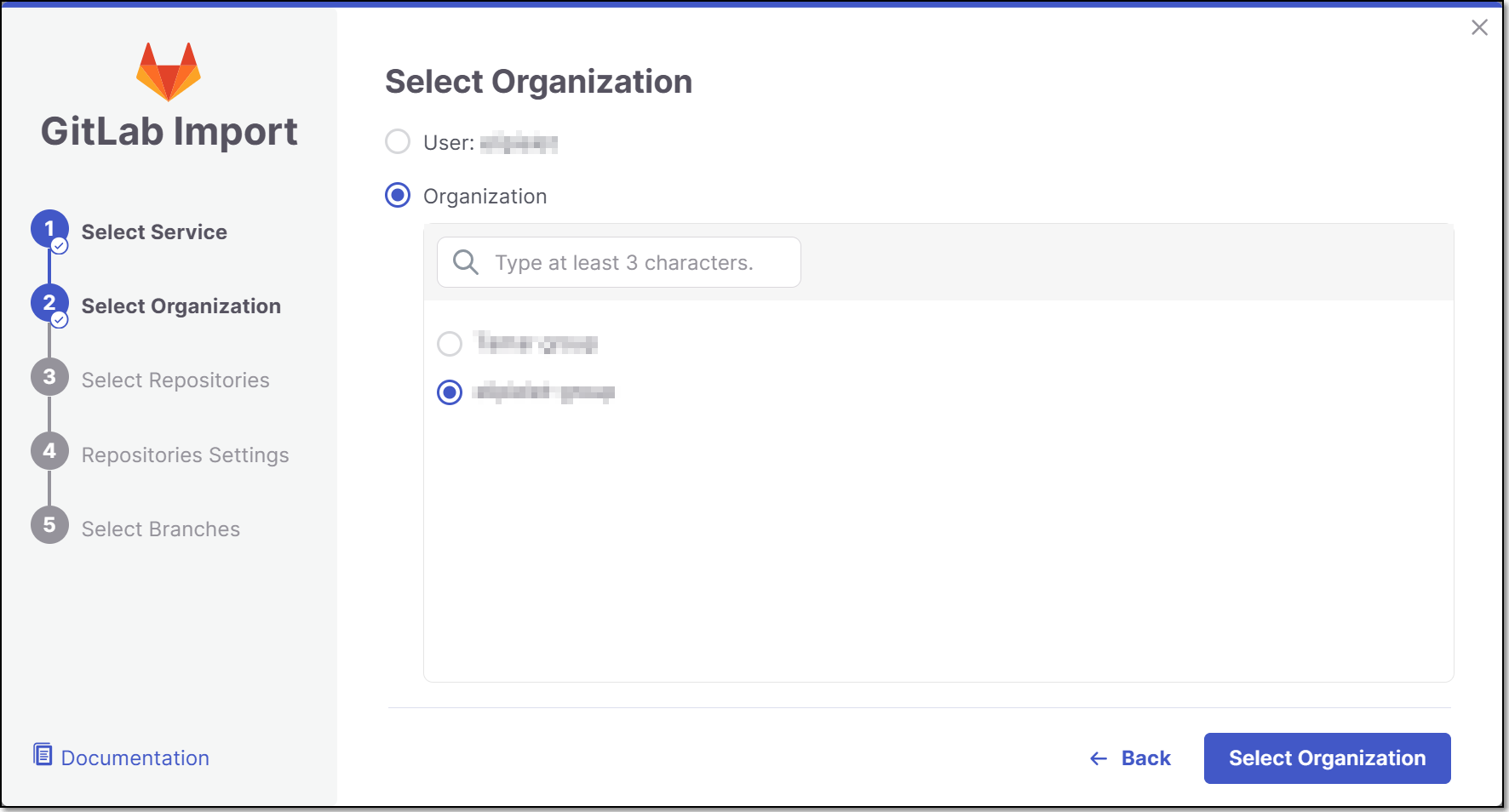
Select the GitLab User/Organization or Group (for the requested repository) and click Select Organization.
The screen contains the following functionalities:
Search bar - Users need to type at least 3 characters of the organization name (GitLab limitation). The search is not case sensitive.
Infinite scroll - For enterprises with a large amount of organizations.
Note
In case you selected GitLab User skip step 5.
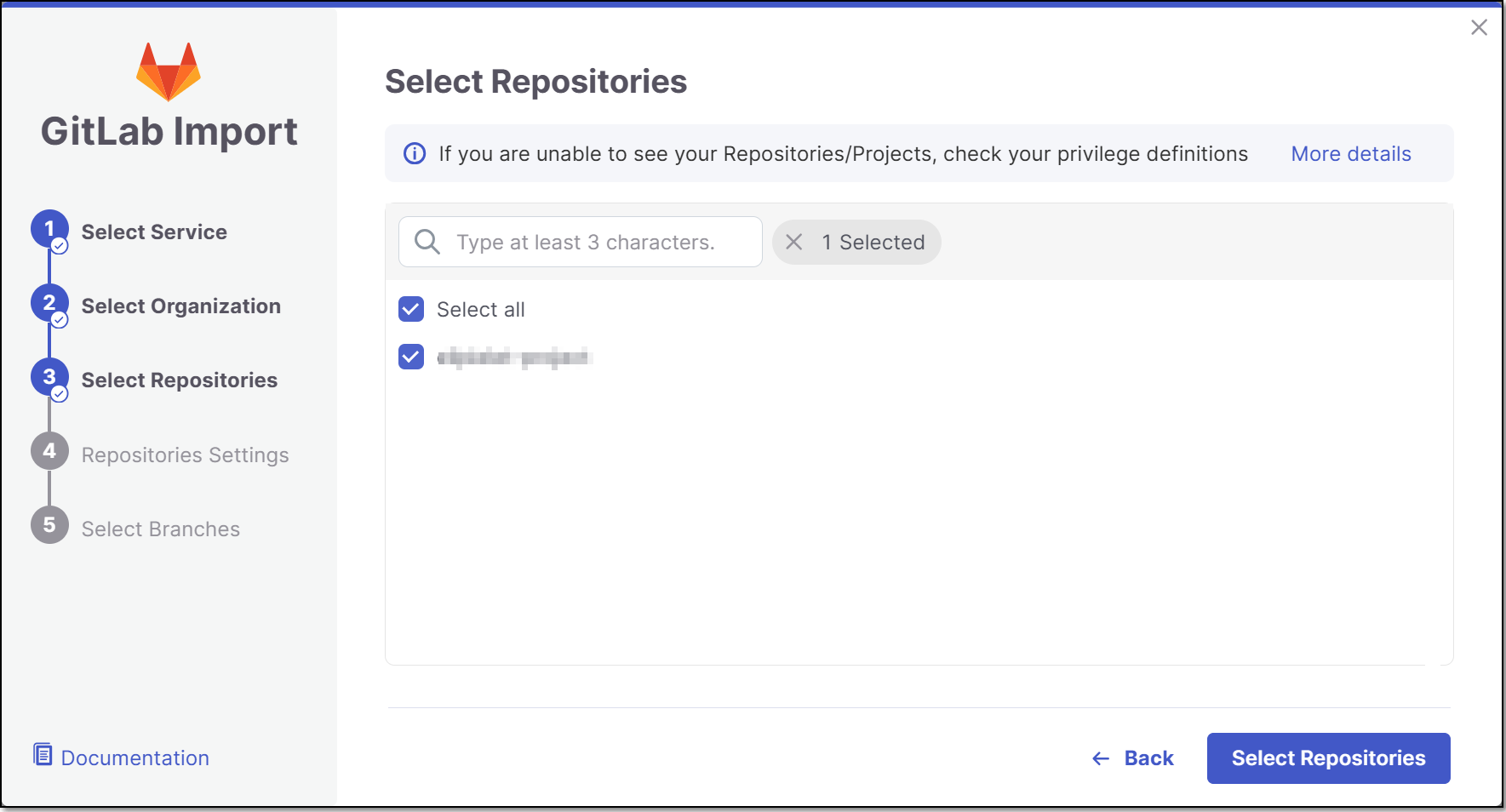
Select Repositories inside the GitLab organization and click Select Repositories.
If the organization contains active repositories, suggested repos will be presented and selected automatically. For additional information see Suggested Repositories.
Note
A separate Checkmarx One Project will be created for each repo that you import.
There can’t be more than one Checkmarx One Project per repo. Therefore, once a Project has been created for a repo, that repo is greyed out in the Import dialog.
In the Repositories Settings step, you can optionally adjust the settings as follows:
If the project has multiple repositories, click All Repositories Settings to adjust the settings for all repositories, or select a specific repository, to adjust the settings for that repository.
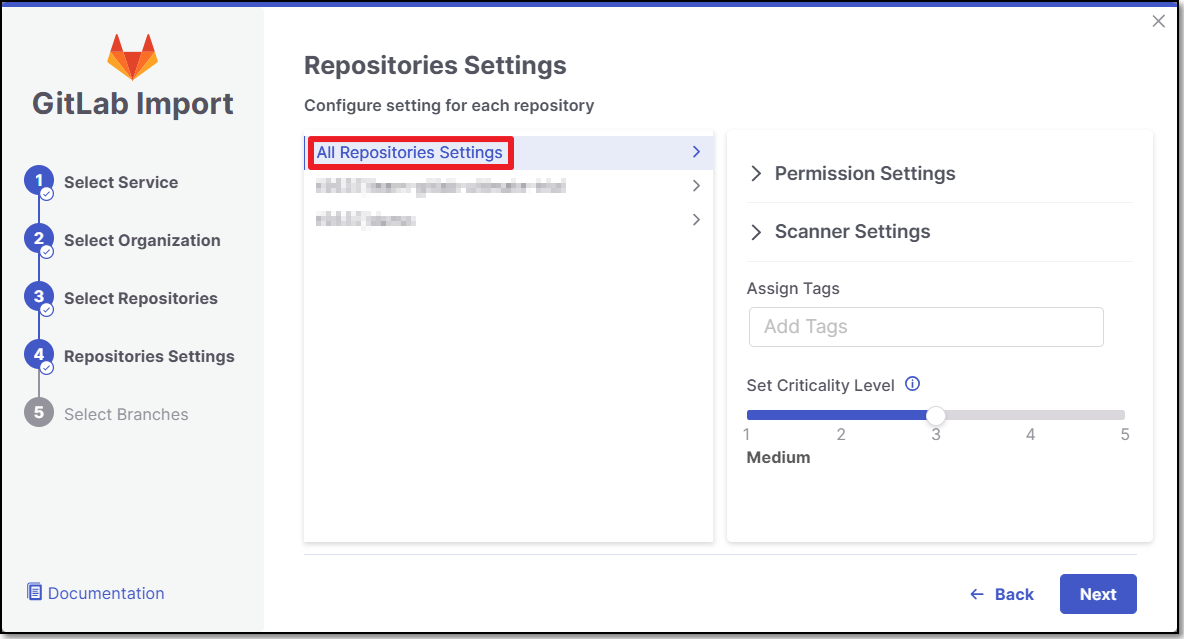
Expand the Permissions Settings and adjust the following settings:
Scan Trigger: Push, Pull request - Automatically trigger a scan when a push event or pull request is done in your SCM. (Default: On)
Pull Request Decoration - Automatically send the scan results summary to the SCM. (Default: On)
SCA Auto Pull Request - Automatically send PRs to your SCM with recommended changes in the manifest file, in order to replace the vulnerable package versions. (Default: Off)
Expand the Scanner Settings and enable the toggle for each scanner you want to use (SAST, SCA, IaC Security, Container Security, API Security, OSSF Scorecard, Secret Detection) for your repositories. At least 1 scanner must be selected for each repository.
Protected Branches (when a specific repository is selected): Specify the branches to be designated as "Protected Branches".
Notice
Specifying a branch as a Protected Branch affects three main areas: scan triggering (for PR and push), policy violation detection, and Feedback App notifications.
COMING SOON: You can also use a wildcard symbol "*" to designate which branches are protected. The wildcard can be used before the string, after the string, or both. All branches that match the wildcard pattern will be treated as protected branches.
Examples:
*→ all branchesrelease*→ branches that begin with "release"*release→ branches that end with "release"* release *→ branches that contain "release" anywhere in the name
Note
For additional information about Protected Branches see About Protected Branches
Add SSH key (when a specific repository is selected).
Assign Tags: Add Tags to the Project. Tags can be added as a simple strings or as key:value pairs.
Set Criticality Level: Manually set the project's criticality level.
Click Next.
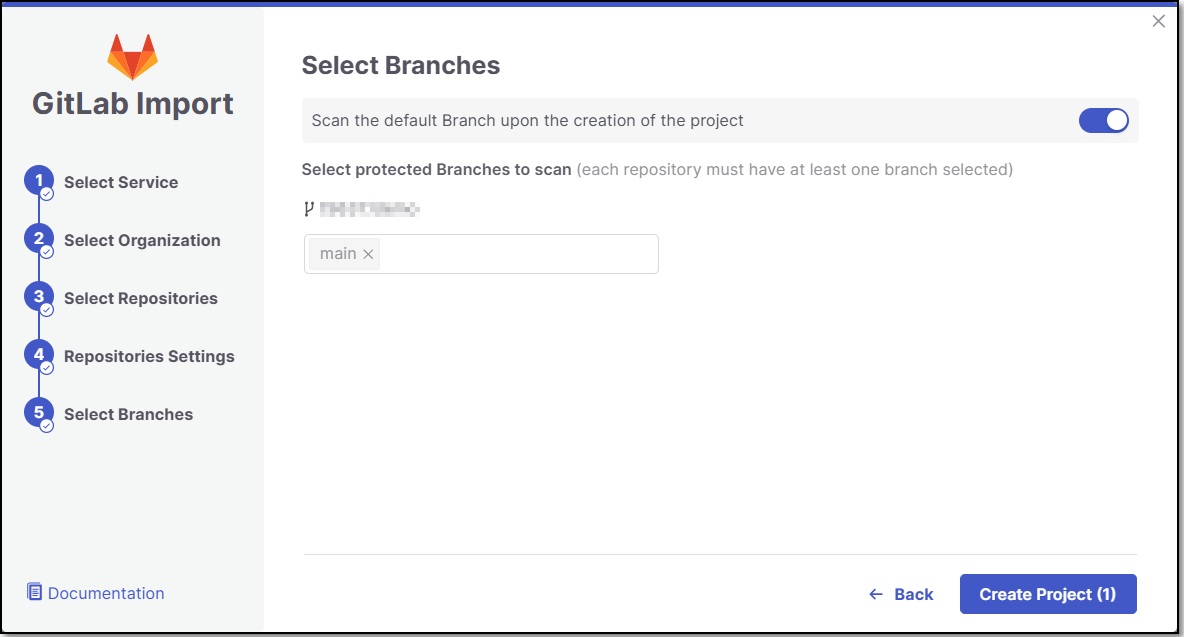
In the Select Branches screen you can decide whether to enable the "Scan the default Branch upon the creation of the project" feature.
For each repository, select the protected branches you want to scan during project creation, and then click Create Project.
Tip
If you specified a wildcard pattern in the previous step, it will not appear as an option on this list.
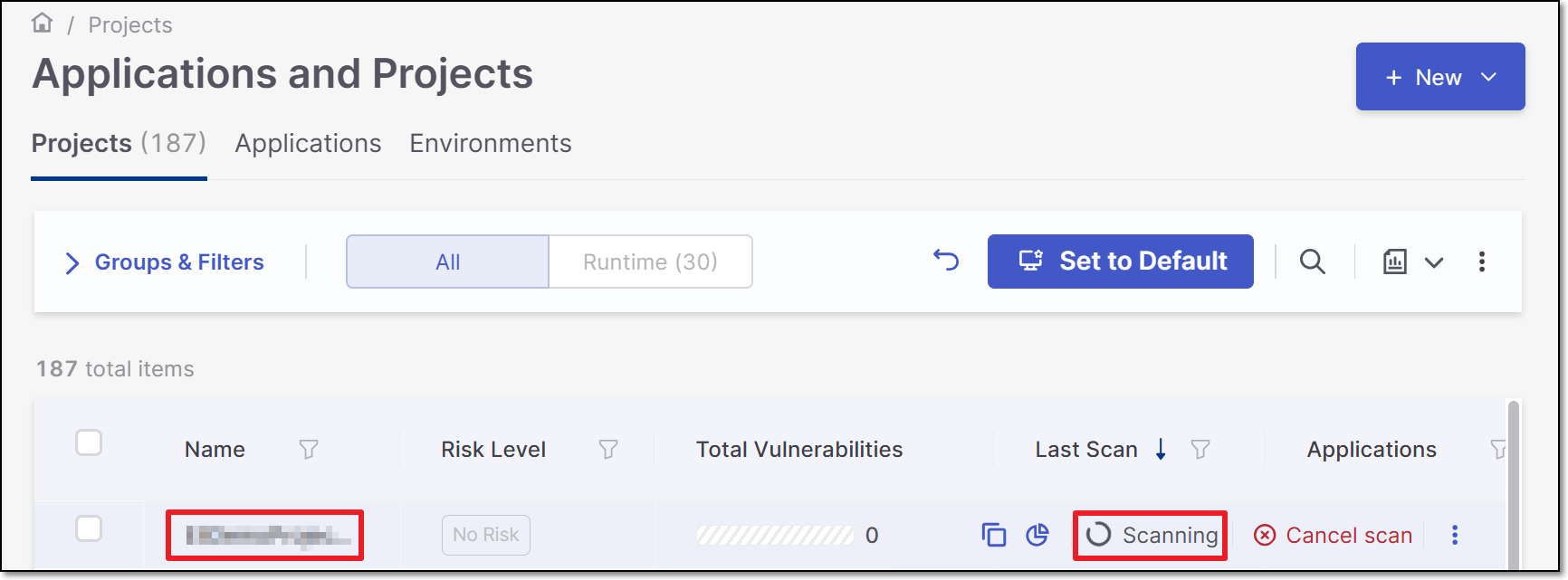
A Project is created for each repository and a scan is initiated for each project. The new projects are displayed on the Projects page,
Note
In order to update the scanners see Imported Project Settings
Editing Project Settings
To learn about editing Project Settings for an existing code repository integration Project, see Code Repository Project Settings.