Single sign-on with OKTA and SAML 2.0 (v9.0.0 and up)
Overview
Checkmarx Access Control supports single sign-on (SSO) logins through SAML 2.0. In our case, the SAML 2.0 identity provider (Idp) is a cloud-based identity and access management service called OKTA. OKTA is compatible with many on premise applications and provides login from the web using existing user credentials.
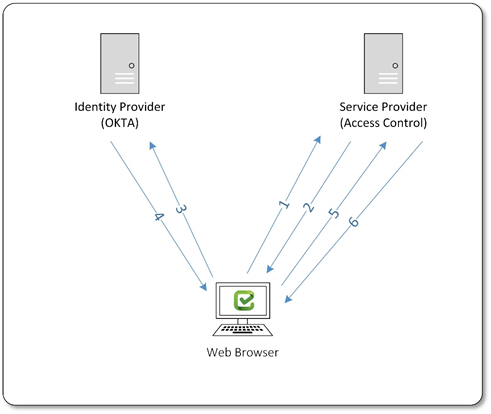
The user issues a request to the Service Provider (Access Control) for a specific resource.
The Service Provider (Access Control) detects that authentication is required and redirects the Web Browser to the Identity Provider (OKTA).
The Web Browser contacts the Identity Provider (OKTA) and is checked for authentication.
Once the user receives authentication, the Identity Provider (OKTA) sends a response (authentication token) back to the Web Browser.
The Web Browser then sends the authentication token to the Service Provider (Access Control).
The Service Provider (Access Control) processes the assertion and the user is automatically logged in.
This document provides a systematic guide for configuring single sign-on using with OKTA and SAML 2.0. Configuring Access Control single sign-on with OKTA consists of exchanging the login details between the Identity Provider (OKTA) and the Service Provider (Access Control) as illustrated in the diagram above.
Notice
Checkmarx ‘Access Control v2.0’ and the ‘Classic UI’ in OKTA are used for the purpose of these instructions. For additional information, click here.
Prerequisites
To set up OKTA to log in to Checkmarx Access Control, the following prerequisites are required:
Checkmarx Access Control (v2.0 is compatible with CxSAST/CxOSA v9.0.0 and later).
Active OKTA account.
Notice
For manual changes that need to be performed within the SAML Identity Provider, for User and Team Attributes, when upgrading to CxSAST v9.x from v8.8\8.9, refer to to Adapting the SAML Identity Provider Attributes when Upgrading CxSAST V8.8 or v8.9 to v9.0 or v9.2.